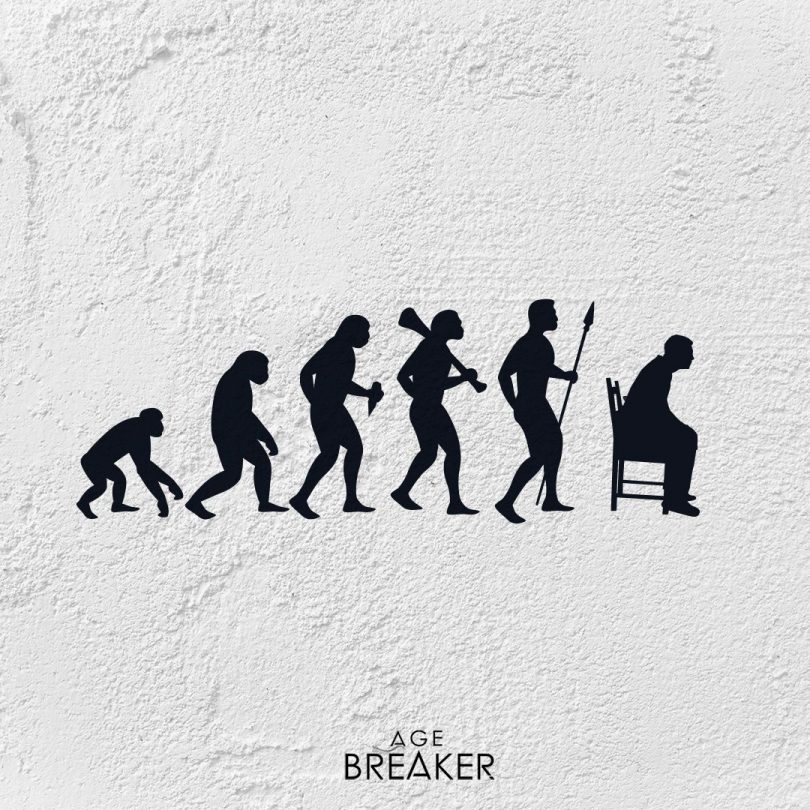
The sitting position, recently universalized, is a factor in aging and age-related diseases.
Result of a long evolutionary process, the human being is exclusively bipedal, the only one of this type among mammals.
Its natural position is standing or lying down, possibly squatting.
Its verticality is a precarious balance that must be constantly adopted or maintained.
The end of the standing man!
According to some statistics, in the United States, over 70% of the population spend 6 hours or more sitting down every day!
How did the idea of sitting down and bending one’s body come about?
A German historian offers an explanation (1):
As man became more sedentary, he gradually adopted the sitting position, a privilege initially reserved for masters and kings – the throne. Then the Benedictines invented the stall, where monks could adopt various positions in the same space.
Then came the church chair, which over time, integrated as objects of prestige the middle-class homes.
Finally, at the end of the 19th century, the sitting position was democratized and sedentarized Europe. In the 20th century, the chair conquered the world and became the symbol of a new type of man: homo sedens, the seated man.
Sitting is neither comfortable nor natural, nor even a rest for the legs. The body finds itself in a position far removed from its physiology.
Numerous studies show that prolonged sitting not only leads to musculoskeletal disorders but is also associated with increased risks of atherosclerosis, development of cardiovascular diseases, certain cancers and, in some cases, premature death.
The mechanisms behind these phenomena are poorly understood, and potentially involve changes in arterial hemodynamics that could lead to oxidative and inflammatory alterations (2).
The sedentary break, a temporary cessation of sitting, has been shown to have a beneficial effect on certain aging factors, such as blood sugar levels and blood pressure.
A study shows that standing for 5 minutes every 30 minutes could be a good dosage (3).
© AGE Breaker updated 07 2024
[Glycation is one of the major causes of aging. Resulting from the fixation of sugars on the proteins constituting the organism, glycation generates toxic compounds that cause cellular aging. Glycation is particularly involved in metabolic disorders, skin aging and cognitive decline.] [AGE BREAKER, patented nutritional supplements, based on rosmarinic acid, recognized by aging specialists around the world for their properties to reverse the effects of glycation.]More on www.agebreaker.com
#agebreaker #glycation #antiaging #longevitymedicine #preventivemedicine #preventivehealth #skinaging #4pmedicine #advancedglycationendproducts
1 : EICKOFF H. La posture assise et les chaises ou la perte de spiritualité (essai). Nov 2001. http://kaempfer.free.fr/Pages/texteshtm/assise.htm
2 : PEKAS, Elizabeth J., ALLEN, Michael F., et PARK, Song-Young. Prolonged sitting and peripheral vascular function: potential mechanisms and methodological considerations. Journal of Applied Physiology, 2023.
https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00730.2022
3: DURAN, Andrea T., FRIEL, Ciaran P., SERAFINI, Maria A., et al. Breaking Up Prolonged Sitting to Improve Cardiometabolic Risk: Dose–Response Analysis of a Randomized Crossover Trial. Medicine, DOI: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000003109